Vue3源码解剖与优化
重要通知
研究与解析Vue3源码的动机,是基于Vue3源码的实现机制,更好地在基础架构与业务具体实现中将代码质量提升到更好的水平,同时能够兼顾更好状态的性能提升,可以充分运用Vue3的核心优势,降低系统设计的冗余与业务实现的臃肿,实现以Vue3生态技术栈为中心的最佳架构设计与业务功能实现。本文档的所有解析与优化,都是基于version: "3.2.33"版本。
Vue3源码基本概况
资源文档
- 官网:https://vuejs.org/
- 中文文档:https://cn.vuejs.org/
- GitHub:https://github.com/vuejs
- mini-vue: https://github.com/cuixiaorui/mini-vue
源码结构与函数关系
// Vue库自调用函数
var Vue = (function (exports) {
let uid = 0;
function createAppAPI(render, hydrate) {
// rootComponent即为Vue.createApp(options)中options参数
return function createApp(rootComponent, rootProps = null) {
const context = createAppContext();
const installedPlugins = new Set();
const app = (context.app = {
_uid: uid++,
_component: rootComponent,
...,
use(plugin, ...options) {},
mixin(mixin) {},
component(name, component) {},
directive(name, directive) {}
// 挂载DOM
mount(rootContainer, isHydrate, isSVG) {
const vnode = createVNode(rootComponent, rootProps);
render(vnode, rootContainer, isSVG);
return getExposeProxy(vnode.component) || vnode.component.proxy;
},
unmount() {},
provide(key, value) {}
}
return app;
}
}
function baseCreateRenderer(options, createHydrationFns) {
const patch = (
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor = null,
parentComponent = null,
parentSuspense = null,
isSVG = false,
slotScopeIds = null,
optimized = isHmrUpdating ? false : !!n2.dynamicChildren,
isRender
) => {};
const render = (vnode, container, isSVG) => {
patch(container._vnode || null, vnode, container, null, null, null, isSVG, null, false, 'isRender');
flushPostFlushCbs();
}
return {
render,
hydrate,
createApp: createAppAPI(render, hydrate)
};
}
function createRenderer(options) {
return baseCreateRenderer(options);
}
const patchProp = (el, key, prevValue, nextValue, isSVG = false, prevChildren, parentComponent, parentSuspense, unmountChildren) => {};
const nodeOps = {};
const rendererOptions = extend({ patchProp }, nodeOps);
let renderer;
function ensureRenderer() {
return (renderer || (renderer = createRenderer(rendererOptions)));
}
const createApp = ((...args) => {
const app = ensureRenderer().createApp(...args);
// 为什么要重写mount方法?不重写会有什么问题?
const { mount } = app;
app.mount = (containerOrSelector) => {
// 获取 document.querySelector(container)
const container = normalizeContainer(containerOrSelector);
const component = app._component;
if (!isFunction(component) && !component.render && !component.template) {
component.template = container.innerHTML;
}
// 清空内容
container.innerHTML = '';
const proxy = mount(container, false, container instanceof SVGElement);
return proxy;
};
return app;
});
exports.createApp = createApp;
Object.defineProperty(exports, '__esModule', { value: true });
return exports;
}({}));
源码目录结构
├─ compiler-core
├─ compiler-dom
├─ compiler-sfc
├─ compiler-ssr
├─ reactivity-transform
├─ reactivity
├─ runtime-core
├─ runtime-dom
├─ runtime-test
├─ server-renderer
├─ sfc-playground
├─ shared
├─ size-check
├─ template-explorer
├─ vue-compat
├─
├─
├─
├─
├─
└─ global.d.ts
Flow静态类型分析器
Rollup构建打包工具
不同构建版本功能
vnode、patch与diff算法
vnode数据结构
// 获取vnode数据结构,rootComponent即为Vue.createApp(options)中options参数,且已经赋值template,即{data:{},render:function(){},template:""}
const vnode = createVNode(rootComponent, rootProps);
const createVNode = (createVNodeWithArgsTransform );
let currentRenderingInstance = null;
let vnodeArgsTransformer;
function transformVNodeArgs(transformer) {
vnodeArgsTransformer = transformer;
}
const createVNodeWithArgsTransform = (...args) => {
return _createVNode(...(vnodeArgsTransformer ? vnodeArgsTransformer(args, currentRenderingInstance) : args));
};
function _createVNode(type, props = null, children = null, patchFlag = 0, dynamicProps = null, isBlockNode = false) {
const shapeFlag = isString(type)
? 1 /* ELEMENT */
: isSuspense(type)
? 128 /* SUSPENSE */
: isTeleport(type)
? 64 /* TELEPORT */
: isObject(type)
? 4 /* STATEFUL_COMPONENT */
: isFunction(type)
? 2 /* FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT */
: 0;
return createBaseVNode(type, props, children, patchFlag, dynamicProps, shapeFlag, isBlockNode, true);
}
function createBaseVNode(
type,
props = null,
children = null,
patchFlag = 0,
dynamicProps = null,
shapeFlag = type === Fragment ? 0 : 1 /* ELEMENT */,
isBlockNode = false,
needFullChildrenNormalization = false
) {
const vnode = {
type, // <null | string | Object>,该值可以是Vue.createApp(options)中options参数值
appContext: null // <null | Object>,
props, // {[key: string]: any},
key: props && normalizeKey(props), // <string | number | null>,唯一标识符
ref: props && normalizeRef(props), // <>,
scopeId: currentScopeId, // <>,
slotScopeIds: null, // <>,
children, // <Array<VNode | string | null> | null>,子节点
component: null, // <ComponentInternalInstance | null>,表示组件实例,如果节点是一个组件,则 component 属性会指向该组件的实例对象。
suspense: null, // <>,
ssContent: null, // <>,
ssFallback: null, // <>,
dirs: null, // <>,
transition: null, // <>,
el: null, // <any>,表示对应的真实 DOM 元素,如果节点已经被渲染到页面上,则 el 属性会指向对应的 DOM 元素。
anchor: null, // <>,vnode是否是已经挂载的节点
target: null, // <>,
targetAnchor: null, // <>,
staticCount: 0, // <>,
shapeFlag, // <>,节点的形状标志
patchFlag, // <>,
dynamicProps, // <string[] | null>,节点的动态事件监听器
dynamicChildren: null, // <Array<VNode | string | null> | null>,节点的动态文本节点
__v_isVNode: true, // <boolean>,
__v_skip: true, // <boolean>,
};
return vnode;
}
patch函数内部设计机制
const Fragment = Symbol('Fragment' );
const Text = Symbol('Text' );
const Comment = Symbol('Comment' );
const Static = Symbol('Static' );
const patch = (
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor = null,
parentComponent = null,
parentSuspense = null,
isSVG = false,
slotScopeIds = null,
optimized = isHmrUpdating ? false : !!n2.dynamicChildren,
isRender
) => {
switch (type) {
case Text:
processText(n1, n2, container, anchor);
break;
case Comment:
processCommentNode(n1, n2, container, anchor);
break;
case Static:
if (n1 == null) {
mountStaticNode(n2, container, anchor, isSVG);
}
else {
patchStaticNode(n1, n2, container, isSVG);
}
break;
case Fragment:
processFragment(n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized);
break;
default:
if (shapeFlag & 1 /* ELEMENT */) {
processElement(n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized);
}
else if (shapeFlag & 6 /* COMPONENT */) {
processComponent(n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized);
}
else if (shapeFlag & 64 /* TELEPORT */) {
type.process(n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized, internals);
}
else if (shapeFlag & 128 /* SUSPENSE */) {
type.process(n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized, internals);
}
else {
warn$1('Invalid VNode type:', type, `(${typeof type})`);
}
}
}
const processComponent = (n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized) => {
if (n1 == null) {
mountComponent(n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized);
} else {
updateComponent(n1, n2, optimized);
}
}
const mountComponent = (initialVNode, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized) => {
const instance = (initialVNode.component = createComponentInstance(initialVNode, parentComponent, parentSuspense));
setupComponent(instance);
setupRenderEffect(instance, initialVNode, container, anchor, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized);
}
const processElement = (n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized) => {
if (n1 == null) {
mountElement(n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized);
}
else {
patchElement(n1, n2, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized);
}
}
diff算法
只比较同级的节点,若找不到与新节点类型相同的节点,则插入一个新节点,若有相同类型的节点则进行节点属性的更新,最后删除新节点列表中不包含的旧节点。Vue3的diff算法的时间复杂度为O(m+n),其中m表示已经存在的元素数量,n表示需要添加或删除的元素数量。
静态提升
Vue 3 在编译阶段会静态提升所有不会改变的节点,这意味着这些节点和它们的子节点会被提升为常量,并且在多次渲染之间重用。这减少了 diff 和重渲染的开销。
预字符串化
对于那些永远不会改变的内容,Vue 3 会在编译时将它们预渲染为静态内容。这样,运行时就不需要为这些内容创建虚拟节点,进一步减少了内存开销和运行时开销。
块树(Block Tree)
Vue 3 引入了块树的概念,将模板分割成多个块(block),每个块对应一部分可以独立更新的 DOM。这使得 Vue 3 可以更精确地跟踪动态节点的变化,仅对需要更新的块进行 diff 和渲染。
双端对比算法
在处理动态列表时,Vue 3 采用了双端对比的策略,这是一种更为高效的 diff 算法。它同时从虚拟 DOM 树的两端(头部和尾部)开始对比,通过找到前后端对应不变的节点,缩小需要进一步对比的范围,减少了对比的次数和复杂度。
初始化指针:设立四个指针,分别指向旧列表的头部(oldStartIdx)和尾部(oldEndIdx),以及新列表的头部(newStartIdx)和尾部(newEndIdx)。
头头对比:比较旧列表头部和新列表头部的节点(oldStartVNode 和 newStartVNode)。如果相同,则将两个指针都向内移动。
尾尾对比:比较旧列表尾部和新列表尾部的节点(oldEndVNode 和 newEndVNode)。如果相同,则将两个指针都向内移动。
头尾对比:比较旧列表头部和新列表尾部的节点。如果相同,表明旧列表的头部节点移动到了尾部,将对应的真实 DOM 节点移动到尾部,并更新指针。
尾头对比:比较旧列表尾部和新列表头部的节点。如果相同,表明新列表的头部节点原来在旧列表的尾部,将对应的真实 DOM 节点移动到头部,并更新指针。
循环对比:重复上述步骤,直到有任意一对开始和结束指针相遇。这个过程中,每次对比后,都会根据对比结果更新指针的位置。
创建新节点和删除旧节点:
- 如果在比较过程结束后,newStartIdx 大于 newEndIdx,表明新列表已经遍历完成,此时旧列表中 oldStartIdx 到 oldEndIdx 之间剩余的节点是多余的,需要被删除。
- 如果 oldStartIdx 大于 oldEndIdx,表明旧列表遍历完成,而新列表中 newStartIdx 到 newEndIdx 之间的节点是新增的,需要创建对应的真实 DOM 节点。
移动和更新:对于上述对比过程中未能匹配的节点,Vue 3 会进一步处理,可能涉及移动已有节点或创建新的节点来匹配新的虚拟 DOM 树结构。
模板字符串渲染工作流程
模板字符串渲染工作流程,即通过声明data数据后,在HTML模板字符串中引用变量,然后触发页面进行渲染data数据后呈现完整视图内容的工作流程。
模板字符串编译原理
- 步骤一:创建一个组件实例。
- 步骤二:解析模板字符串,并将其转换为一个 AST(抽象语法树)。
- 解析模板字符串,将其转换为一个数组。
- 遍历数组,将每个元素转换为一个节点。
- 根据节点的类型和属性,构建 AST。
- 步骤三:对 AST 进行优化和转换,生成最终的渲染函数。
- 删除空节点。
- 合并相邻的文本节点。
- 提取公共子树。
- 步骤四:在组件的生命周期钩子函数中调用渲染函数,生成最终的 UI 界面。
创建一个应用示例
- 模板语法
<div id="app">
<section class="vue-source-wrapper">
{{ title }}
</section>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
title: 'Vue3.x源码'
}
},
});
app.mount('#app');
</script>
- 渲染函数
h() 是 hyperscript 的简称——意思是“能生成 HTML (超文本标记语言) 的 JavaScript”。
import { h } from 'vue';
const vnode = h(
'div', // type
{ // props,attribute 和 property 都能在 prop 中书写
id: 'foo',
class: 'bar',
onClick: () => {},
class: [foo, { bar }], style: { color: 'red' }
},
[
// children 数组可以同时包含 vnodes 与字符串
'hello',
h('span', 'hello')
]
)
- JSX语法
JSX 是 JavaScript 的一个类似 XML 的扩展。
const vnode = <div id={dynamicId}>hello, {userName}</div>;
核心函数调度依赖关系图
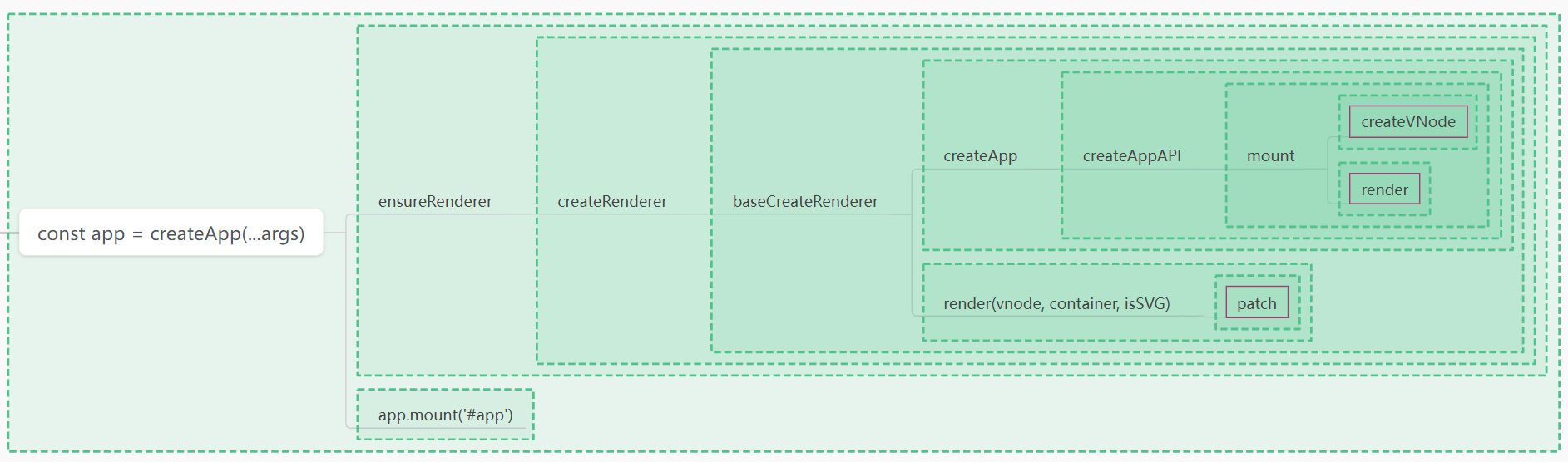 |
挂载DOM呈现视图内容
const mountElement = (vnode, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized) => {
let el;
const { type, props, shapeFlag, transition, patchFlag, dirs } = vnode;
el = vnode.el = hostCreateElement(vnode.type, isSVG, props && props.is, props);
// 此处实现挂载DOM
hostInsert(el, container, anchor);
}
数据更新渲染工作流程
数据更新渲染工作流程,即更新数据内容后,页面呈现完整UI内容渲染的工作流程。
数据更新业务代码
<div id="app">
<section class="vue-source-wrapper">
{{ title }}
</section>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
title: 'Vue3源码解析'
}
},
methods: {
updateData() {
this.title = 'Vue3源码优化';
}
},
created() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.updateData();
}, 3000);
}
});
app.mount('#app');
</script>
建立数据更新依赖关系
function applyOptions(instance) {
const options = resolveMergedOptions(instance);
const publicThis = instance.proxy;
const { data } = options;
const data = dataOptions.call(publicThis, publicThis);
instance.data = reactive(data);
}
function createGetter(isReadonly = false, shallow = false) {
return function get(target, key, receiver) {
const res = Reflect.get(target, key, receiver);
return res;
}
}
function createSetter(shallow = false) {
return function set(target, key, value, receiver) {
let oldValue = target[key];
const result = Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver);
if (!hadKey) {
trigger(target, "add" /* ADD */, key, value);
}
else if (hasChanged(value, oldValue)) {
trigger(target, "set" /* SET */, key, value, oldValue);
}
return result;
}
}
const get = /*#__PURE__*/ createGetter();
const set = /*#__PURE__*/ createSetter();
const mutableHandlers = {
get,
set,
deleteProperty,
has,
ownKeys
};
function createInstrumentationGetter(isReadonly, shallow) {
return (target, key, receiver) => {
return Reflect.get(hasOwn(instrumentations, key) && key in target
? instrumentations
: target, key, receiver);
}
}
const mutableCollectionHandlers = {
get: /*#__PURE__*/ createInstrumentationGetter(false, false)
};
const reactiveMap = new WeakMap();
function reactive(target) {
return createReactiveObject(target, false, mutableHandlers, mutableCollectionHandlers, reactiveMap);
}
function createReactiveObject(target, isReadonly, baseHandlers, collectionHandlers, proxyMap) {
const proxy = new Proxy(target, targetType === 2 /* COLLECTION */ ? collectionHandlers : baseHandlers);
proxyMap.set(target, proxy);
return proxy;
}
建立数据更新触发机制
function createSetter(shallow = false) {
return function set(target, key, value, receiver) {
let oldValue = target[key];
const result = Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver);
if (!hadKey) {
trigger(target, "add" /* ADD */, key, value);
}
else if (hasChanged(value, oldValue)) {
trigger(target, "set" /* SET */, key, value, oldValue);
}
return result;
}
}
const targetMap = new WeakMap();
function trigger(target, type, key, newValue, oldValue, oldTarget) {
const depsMap = targetMap.get(target);
let deps = [];
// 不同条件不同逻辑,此处仅仅列出其中一个
deps.push(depsMap.get(ITERATE_KEY));
const eventInfo = { target, type, key, newValue, oldValue, oldTarget }
triggerEffects(deps[0], eventInfo);
}
function triggerEffects(dep, debuggerEventExtraInfo) {
for (const effect of isArray(dep) ? dep : [...dep]) {
if (effect !== activeEffect || effect.allowRecurse) {
if (effect.onTrigger) {
effect.onTrigger(extend({ effect }, debuggerEventExtraInfo));
}
if (effect.scheduler) {
effect.scheduler();
}
else {
effect.run();
}
}
}
}
ReactiveEffect
const setupRenderEffect = (instance, initialVNode, container, anchor, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized) => {
const componentUpdateFn = () => {
const nextTree = renderComponentRoot(instance);
const prevTree = instance.subTree;
patch(prevTree, nextTree, hostParentNode(prevTree.el), getNextHostNode(prevTree), instance, parentSuspense, isSVG);
}
const effect = (instance.effect = new ReactiveEffect(componentUpdateFn, () => queueJob(instance.update), instance.scope));
const update = (instance.update = effect.run.bind(effect));
update();
}
class ReactiveEffect {
constructor(fn, scheduler = null, scope) {
this.fn = fn;
this.scheduler = scheduler;
this.active = true;
this.deps = [];
this.parent = undefined;
recordEffectScope(this, scope);
}
run() {
if (!this.active) {
return this.fn();
}
}
stop() {}
}
const queue = [];
function queueJob(job) {
if ((!queue.length ||
!queue.includes(job, isFlushing && job.allowRecurse ? flushIndex + 1 : flushIndex)) &&
job !== currentPreFlushParentJob) {
if (job.id == null) {
queue.push(job);
}
else {
queue.splice(findInsertionIndex(job.id), 0, job);
}
queueFlush();
}
}
const resolvedPromise = /*#__PURE__*/ Promise.resolve();
function queueFlush() {
if (!isFlushing && !isFlushPending) {
isFlushPending = true;
currentFlushPromise = resolvedPromise.then(flushJobs);
}
}
派发更新
set()
trigger()
triggerEffect()
effect.scheduler()
queueJob(update)
queueFlush()
flushJobs()
effect.run()
effect.fn()
componentUpdateFn()
patch()
监听器Observer
订阅者Watcher
组件渲染工作流程
Compiler编译机制
AST主要包括三个部分:模板编译、优化和渲染。模板编译是将模板转换为 AST 的过程。渲染是将 JavaScript 代码转换为实际的 UI 元素的过程。
将template解析成AST
const decodeRE = /&(gt|lt|amp|apos|quot);/g;
const decodeMap = {
gt: '>',
lt: '<',
amp: '&',
apos: "'",
quot: '"'
};
registerRuntimeCompiler(compileToFunction);
function registerRuntimeCompiler(_compile) {
compile = _compile;
installWithProxy = i => {
if (i.render._rc) {
i.withProxy = new Proxy(i.ctx, RuntimeCompiledPublicInstanceProxyHandlers);
}
};
}
function compileToFunction(template, options) {
const { code } = compile$1(template, extend({
hoistStatic: true,
onError: onError,
onWarn: e => onError(e, true)
}, options));
const render = (new Function(code)());
render._rc = true;
return (compileCache[key] = render);
}
function compile$1(template, options = {}) {
return baseCompile(template, extend({}, parserOptions, options, {
nodeTransforms: [
ignoreSideEffectTags,
...DOMNodeTransforms,
...(options.nodeTransforms || [])
],
directiveTransforms: extend({}, DOMDirectiveTransforms, options.directiveTransforms || {}),
transformHoist: null
}));
}
function baseCompile(template, options = {}) {
const ast = isString(template) ? baseParse(template, options) : template;
const [nodeTransforms, directiveTransforms] = getBaseTransformPreset();
transform(ast, extend({}, options, {
prefixIdentifiers,
nodeTransforms: [
...nodeTransforms,
...(options.nodeTransforms || []) // user transforms
],
directiveTransforms: extend({}, directiveTransforms, options.directiveTransforms || {} // user transforms
)
}));
return generate(ast, extend({}, options, {
prefixIdentifiers
}));
}
function baseParse(content, options = {}) {
const context = createParserContext(content, options);
const start = getCursor(context);
return createRoot(parseChildren(context, 0 /* DATA */, []), getSelection(context, start));
}
function transform(root, options) {
const context = createTransformContext(root, options);
traverseNode(root, context);
if (options.hoistStatic) {
hoistStatic(root, context);
}
if (!options.ssr) {
createRootCodegen(root, context);
}
// finalize meta information
root.helpers = [...context.helpers.keys()];
root.components = [...context.components];
root.directives = [...context.directives];
root.imports = context.imports;
root.hoists = context.hoists;
root.temps = context.temps;
root.cached = context.cached;
}
function generate(ast, options = {}) {
const context = createCodegenContext(ast, options);
return {
ast,
code: context.code,
preamble: ``,
// SourceMapGenerator does have toJSON() method but it's not in the types
map: context.map ? context.map.toJSON() : undefined
};
}
function parseChildren(context, mode, ancestors) {
const parent = last(ancestors);
const ns = parent ? parent.ns : 0 /* HTML */;
const nodes = [];
while (!isEnd(context, mode, ancestors)) {
//
}
return removedWhitespace ? nodes.filter(Boolean) : nodes;
}
AST优化
code generate代码生成
在代码生成阶段中,编译器将根据优化过的 AST 生成可执行的渲染函数。
解析模板字符串过程
解析模板字符串:首先,Vue3 将模板字符串解析成一个抽象语法树(AST)。这个 AST 表示模板字符串的结构和语法。 生成渲染函数:然后,Vue3 根据解析后的 AST 生成一个渲染函数。这个渲染函数将模板中的数据和逻辑与组件实例的属性和方法进行绑定。 渲染视图:最后,在组件实例的生命周期钩子函数mounted中,调用渲染函数将模板渲染成实际的视图。 解析模板字符串的具体过程包括词法分析、语法分析和生成代码等步骤。
AST 在 Vue3 模板渲染过程中主要有以下几个步骤: 词法分析:首先,Vue3 会将模板字符串进行词法分析,将其分解成一个个的词法单元,例如标签、属性、文本等。 语法分析:然后,Vue3 会进行语法分析,将词法单元组合成一个语法树。这个语法树表示了模板字符串的语法结构和元素之间的关系。 生成代码:最后,Vue3 会根据语法树生成渲染函数的代码。这个代码将模板中的数据和逻辑与组件实例的属性和方法进行绑定,以便在运行时高效地执行。 通过使用 AST,Vue3 可以更加高效地处理模板字符串,并且可以提供更多的语法特性和功能,例如模板表达式、条件语句、循环语句等。同时,AST 还可以方便地进行模板的静态分析和优化,以提高模板的性能和效率。
AST在Vue3模板渲染过程中进行模板的静态分析和优化 模板编译优化:通过对模板进行静态分析和优化,可以减少模板的编译时间和代码体积。例如,可以删除模板中不必要的元素,合并相邻的元素等。 数据绑定优化:通过对模板进行静态分析和优化,可以减少数据绑定的次数和开销。例如,可以将多个数据绑定合并成一个,以减少数据传递的次数。 性能优化:通过对模板进行静态分析和优化,可以提高模板的性能和效率。例如,可以将一些计算和操作提前进行,以减少运行时的计算量。
Runtime运行时系统
Reactivity响应式系统
模板引擎
性能问题
- 模板的大小和复杂度:如果模板非常大,并且包含许多复杂的逻辑和表达式,那么解析和渲染模板的时间可能会比较长。
- 数据的大小和复杂度:如果数据非常大,并且需要进行大量的计算和处理,那么生成 HTML 内容的时间可能会比较长。
- 模板引擎的实现方式:不同的模板引擎实现方式可能会对性能产生不同的影响。例如,一些模板引擎可能会使用编译的方式来生成 HTML 内容,而另一些模板引擎可能会在运行时动态生成 HTML 内容。
Vue3 生命周期与相关钩子
基础方法
callHook(options.beforeCreate, instance, "bc" /* BEFORE_CREATE */);
beforeCreate
created
beforeMount
mounted
beforeUpdate
updated
beforeUnmount
unmounted
errorCaptured
renderTracked
renderTriggered
activated
deactivated
serverPrefetch
Vue3 Event事件系统
Vue3指令系统
源码实现
function createAppAPI(render, hydrate) {
return function createApp(rootComponent, rootProps = null) {
const context = createAppContext();
const app = (context.app = {
directive(name, directive) {
{
validateDirectiveName(name);
}
if (!directive) {
return context.directives[name];
}
if (context.directives[name]) {
warn$1(`Directive "${name}" has already been registered in target app.`);
}
context.directives[name] = directive;
return app;
}
})
return app;
}
}
function createAppContext() {
return {
directives: {}
}
}
function setupStatefulComponent(instance, isSSR) {
const Component = instance.type;
if (Component.directives) {
const names = Object.keys(Component.directives);
for (let i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
validateDirectiveName(names[i]);
}
}
}
v-model指令的实现原理
v-if与v-show的实现原理
v-for的实现原理,以及key的作用
插件系统
安装引入
import { createApp } from 'vue'
const app = createApp({})
app.use(myPlugin, {
/* 可选的选项 */
})
Vue插件源码结构
const installedPlugins = new Set();
const app = (context.app = {
_uid: uid++,
version,
use(plugin, ...options) {
if (installedPlugins.has(plugin)) {
warn$1(`Plugin has already been applied to target app.`);
}
else if (plugin && isFunction(plugin.install)) {
installedPlugins.add(plugin);
plugin.install(app, ...options);
}
else if (isFunction(plugin)) {
installedPlugins.add(plugin);
plugin(app, ...options);
}
else {
warn$1(`A plugin must either be a function or an object with an "install" ` +
`function.`);
}
return app;
},
});
Vuex 源码实现
Store.prototype.install = function install (app, injectKey) {
app.provide(injectKey || storeKey, this);
app.config.globalProperties.$store = this;
var useDevtools = this._devtools !== undefined
? this._devtools
: true ;
if (useDevtools) {
addDevtools(app, this);
}
};
Runtime运行时
Vue3 reactivity响应式系统
代码示例
Vue3 component组件系统
组件实例 Instance
function createComponentInstance(vnode, parent, suspense) {
const type = vnode.type;
// inherit parent app context - or - if root, adopt from root vnode
const appContext = (parent ? parent.appContext : vnode.appContext) || emptyAppContext;
const instance = {
uid: uid$1++,
vnode,
type,
parent,
appContext,
root: null,
next: null,
subTree: null,
effect: null,
update: null,
scope: new EffectScope(true /* detached */),
render: null,
proxy: null,
exposed: null,
exposeProxy: null,
withProxy: null,
provides: parent ? parent.provides : Object.create(appContext.provides),
accessCache: null,
renderCache: [],
// local resovled assets
components: null,
directives: null,
// resolved props and emits options
propsOptions: normalizePropsOptions(type, appContext),
emitsOptions: normalizeEmitsOptions(type, appContext),
// emit
emit: null,
emitted: null,
// props default value
propsDefaults: EMPTY_OBJ,
// inheritAttrs
inheritAttrs: type.inheritAttrs,
// state
ctx: EMPTY_OBJ,
data: EMPTY_OBJ,
props: EMPTY_OBJ,
attrs: EMPTY_OBJ,
slots: EMPTY_OBJ,
refs: EMPTY_OBJ,
setupState: EMPTY_OBJ,
setupContext: null,
// suspense related
suspense,
suspenseId: suspense ? suspense.pendingId : 0,
asyncDep: null,
asyncResolved: false,
// lifecycle hooks
// not using enums here because it results in computed properties
isMounted: false,
isUnmounted: false,
isDeactivated: false,
bc: null,
c: null,
bm: null,
m: null,
bu: null,
u: null,
um: null,
bum: null,
da: null,
a: null,
rtg: null,
rtc: null,
ec: null,
sp: null
};
{
instance.ctx = createDevRenderContext(instance);
}
instance.root = parent ? parent.root : instance;
instance.emit = emit$1.bind(null, instance);
// apply custom element special handling
if (vnode.ce) {
vnode.ce(instance);
}
return instance;
}
核心API设计
nextTick
基于
const resolvedPromise = Promise.resolve();
let currentFlushPromise = null;
function nextTick(fn) {
const p = currentFlushPromise || resolvedPromise;
return fn ? p.then(this ? fn.bind(this) : fn) : p;
}
function queueFlush() {
if (!isFlushing && !isFlushPending) {
isFlushPending = true;
currentFlushPromise = resolvedPromise.then(flushJobs);
}
}
KeepAlive
data函数对象
注意事项
data必须声明为Function,源码已经对其进行限制约束。
const { data: dataOptions } = options;
if (!isFunction(dataOptions)) {}
const data = dataOptions.call(publicThis, publicThis);
if (isPromise(data)) {}
if (!isObject(data)) {}
instance.data = reactive(data);
{
for (const key in data) {
checkDuplicateProperties("Data" /* DATA */, key);
// expose data on ctx during dev
if (!isReservedPrefix(key[0])) {
Object.defineProperty(ctx, key, {
configurable: true,
enumerable: true,
get: () => data[key],
set: NOOP
});
}
}
}